前面我们已经学习了如何开发一个 MCP 服务器和客户端,但是整个过程要求我们要有一定的开发经验,这对于初学者来说有一定的难度。
今天我们来为大家讲解一个直接使用 LLM 来开发 MCP 服务器的方案。
准备工作
首先我们需要准备一些文档,这些文档可以帮助 LLM 更好的理解 MCP 协议,当然我们也可以直接将 MCP 的官方文档提供给 LLM。
这里我们使用 Cursor 来直接开发,并提供 https://modelcontextprotocol.io/llms-full.txt 文件作为文档内容,这里我们下载到本地 llms-full.txt 文件。
然后就可以打开 Cursor 开始开发了。
开始开发
我们只需要向 Cursor 描述清楚想要构建的服务器类型即可:
服务器将暴露哪些资源 将提供哪些工具 应包含哪些提示 需要与哪些外部系统交互
这里我们还是以前面和大家讲解的天气查询为例,来为大家演示如何使用 LLM 来开发一个 MCP 服务器。
打开 Cursor 聊天窗口,并使用 @ 命令选择 llms-full.txt 文件,然后和 Cursor 对话描述清楚需求:
Build a weather query MCP server that: - Developed using TypeScript - Connects to the OpenWeatherMap API to fetch weather information - Obtains the OpenWeatherMap API key from the environment variable `OPENWEATHERMAP_API_KEY` - Provides two tools: one for querying current weather of a specified city, and another for forecasting weather for the next few days - Retrieves weather data as comprehensive as possible

这里我们选择使用 Cluade-3.7-sonnet 模型,然后点击 Send 按钮,等待片刻,就可以看到 Cursor 开始根据我们的需求生成代码了。
我们可以先从核心功能开始,然后逐步添加更多功能。在遇到任何问题时,都可以向 Cursor 提问 解决,最后还可以让 Cursor 帮助我们来测试服务器并处理边界情况。
最后我们就可以得到一个完整的 MCP 服务器代码了,如下所示:
import { McpServer } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js"; import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js"; import { z } from "zod"; import { writeFileSync } from "fs"; // Setup debugging to file instead of stdout const debugLog = (message: string) => { try { writeFileSync( "weather-mcp-debug.log", `${new Date().toISOString()}: ${message}\n`, { flag: "a" } ); } catch (e) { // Silently fail if we can't write to the log file } }; // Check if API key is present const OPENWEATHERMAP_API_KEY = process.env.OPENWEATHERMAP_API_KEY; if (!OPENWEATHERMAP_API_KEY) { debugLog("Error: OPENWEATHERMAP_API_KEY environment variable is not set"); process.exit(1); } const BASE_URL = "https://api.openweathermap.org"; // Create an MCP server const server = new McpServer({ name: "WeatherMCP", version: "1.0.0", }); // Helper function to fetch weather data from OpenWeatherMap API async function fetchWeatherData( endpoint: string, params: Record<string, string> ) { const url = new URL(`/data/2.5/${endpoint}`, BASE_URL); // We've already checked if the API key exists, so we can safely assert it's not undefined const apiKey = OPENWEATHERMAP_API_KEY as string; url.searchParams.append("appid", apiKey); // Add all parameters to the URL Object.entries(params).forEach(([key, value]) => { url.searchParams.append(key, value); }); try { // Hide the API key in logs const sanitizedUrl = url.toString().replace(apiKey, "API_KEY_HIDDEN"); debugLog(`Fetching from URL: ${sanitizedUrl}`); const response = await fetch(url); if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`API error: ${response.status} ${response.statusText}`); } return await response.json(); } catch (error) { debugLog( `Error fetching weather data: ${ error instanceof Error ? error.message : String(error) }` ); throw error; } } // Format weather data to a human-readable format function formatCurrentWeather(data: any) { const main = data.main; const weather = data.weather[0]; const wind = data.wind; const sys = data.sys; return ` Current Weather in ${data.name}, ${sys.country}: Description: ${weather.main} (${weather.description}) Temperature: ${(main.temp - 273.15).toFixed(1)}°C / ${( ((main.temp - 273.15) * 9) / 5 + 32 ).toFixed(1)}°F Feels Like: ${(main.feels_like - 273.15).toFixed(1)}°C Humidity: ${main.humidity}% Pressure: ${main.pressure} hPa Wind: ${wind.speed} m/s, Direction: ${wind.deg}° Visibility: ${data.visibility / 1000} km Cloudiness: ${data.clouds.all}% Sunrise: ${new Date(sys.sunrise * 1000).toLocaleTimeString()} Sunset: ${new Date(sys.sunset * 1000).toLocaleTimeString()} `.trim(); } function formatForecast(data: any, days: number) { const city = data.city; let forecast = `${days}-day Forecast for ${city.name}, ${city.country}:\n\n`; // Group forecast by day const dailyForecasts: Record<string, any[]> = {}; data.list.forEach((item: any) => { const date = new Date(item.dt * 1000); const day = date.toDateString(); if (!dailyForecasts[day]) { dailyForecasts[day] = []; } dailyForecasts[day].push(item); }); // Format each day's forecast Object.entries(dailyForecasts).forEach(([day, items]) => { forecast += `${day}:\n`; items.forEach((item) => { const time = new Date(item.dt * 1000).toLocaleTimeString([], { hour: "2-digit", minute: "2-digit", }); const temp = (item.main.temp - 273.15).toFixed(1); const description = item.weather[0].description; const humidity = item.main.humidity; const windSpeed = item.wind.speed; forecast += ` ${time}: ${temp}°C, ${description}, Humidity: ${humidity}%, Wind: ${windSpeed} m/s\n`; }); forecast += "\n"; }); return forecast.trim(); } // Tool: Get current weather for a city server.tool( "current_weather", { city: z.string().describe("City name (e.g., 'London' or 'New York,US')"), units: z .enum(["metric", "imperial", "standard"]) .optional() .describe("Units of measurement (metric, imperial, or standard)"), }, async ({ city, units = "metric" }) => { try { debugLog(`Processing current weather request for ${city}`); const data = await fetchWeatherData("weather", { q: city, units: units, }); return { content: [ { type: "text", text: formatCurrentWeather(data), }, ], }; } catch (error) { const errorMessage = error instanceof Error ? error.message : String(error); debugLog(`Error in current_weather tool: ${errorMessage}`); return { content: [ { type: "text", text: `Error fetching weather data: ${errorMessage}`, }, ], isError: true, }; } } ); // Tool: Get weather forecast for a city server.tool( "weather_forecast", { city: z.string().describe("City name (e.g., 'London' or 'New York,US')"), days: z .number() .min(1) .max(5) .optional() .describe("Number of days for forecast (1-5)"), units: z .enum(["metric", "imperial", "standard"]) .optional() .describe("Units of measurement (metric, imperial, or standard)"), }, async ({ city, days = 5, units = "metric" }) => { try { debugLog(`Processing forecast request for ${city}, ${days} days`); const data = await fetchWeatherData("forecast", { q: city, units: units, cnt: String(days * 8), // 8 forecasts per day (3-hour steps) }); return { content: [ { type: "text", text: formatForecast(data, days), }, ], }; } catch (error) { const errorMessage = error instanceof Error ? error.message : String(error); debugLog(`Error in weather_forecast tool: ${errorMessage}`); return { content: [ { type: "text", text: `Error fetching forecast data: ${errorMessage}`, }, ], isError: true, }; } } ); // Start receiving messages on stdin and sending messages on stdout debugLog("Starting Weather MCP server"); try { const transport = new StdioServerTransport(); await server.connect(transport); } catch (error) { debugLog( `Error starting server: ${ error instanceof Error ? error.message : String(error) }` ); process.exit(1); }
从上面代码可以看出同样我们实现了两个工具:
current_weather:查询当前天气weather_forecast:查询未来天气预报
然后用同样的方法将这个服务器代码先进行构建:
# 使用 tsc 进行构建 tsc # 使用 npm 进行构建 # npm run build
构建后的代码会保存到 build/index.js 文件中。
接下来我们可以在当前目录下创建一个 .cursor/mcp.json 文件,并配置好服务器信息:
{ "mcpServers": { "weather": { "command": "node", "args": ["/path/to/weather-mcp-server/build/index.js"], "env": { "OPENWEATHERMAP_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY_HERE" } } } }
在最新的 Cursor 版本(Version: 0.48.6)中,当我们添加了 MCP 配置后,会自动检测到新增了 MCP server,会提示我们是否开启:
开启后中 Cursor 设置页面也可以看到我们新增的两个工具:

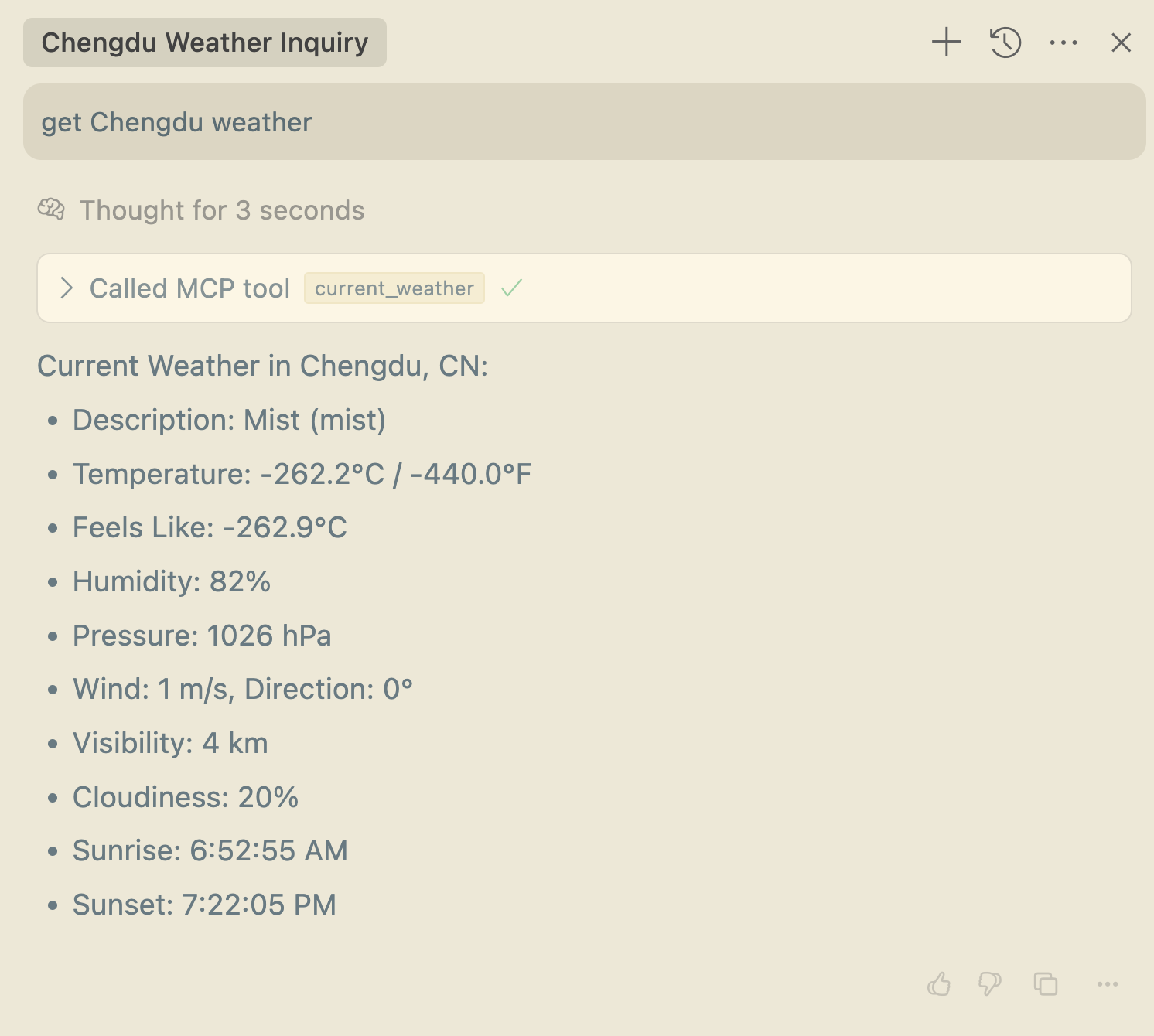
然后我们就可以在 Cursor 中来询问天气信息了:
最佳实践
上面我们介绍的只是一个简单的 MCP 服务器,实际使用中我们可能需要根据实际需求来构建更加复杂的服务器。
在使用 Cursor 或者 LLM 构建 MCP 服务器时,我们可以参考以下最佳实践:
- 将复杂的服务器拆分为更小的部分
- 在继续下一步之前,彻底测试每个组件
- 考虑安全性 - 验证输入并适当地限制访问
- 为将来的维护做好充分的代码文档
- 严格遵循 MCP 协议规范
在构建好服务器后:
- 仔细审查生成的代码
- 使用 MCP Inspector 工具测试服务器
- 将服务器连接到 MCP 客户端 测试
- 根据实际使用和反馈进行迭代
请记住,随着需求的变化,LLM 可以帮助我们修改和改进服务器。
还需要更多指导?只需向 LLM 提出关于实现 MCP 功能或解决出现的问题的具体问题,当然 MCP 客户端的实现也可以交给 LLM 来完成。

